Dynamic Binding, also known as late binding, is a programming mechanism where the method to be called is determined at runtime, not during compile-time. It is a key part of polymorphism in object-o...
Dynamic Binding, also known as late binding, is a programming mechanism where the method to be called is determined at runtime, not during compile-time. It is a key part of polymorphism in object-oriented programming, allowing objects to be handled more generically.
For example, a base class pointer can refer to objects of derived classes, and the correct method is chosen based on the object's type at runtime.
Benefits of Dynamic Binding:
- Enhances flexibility and extensibility, as new classes and methods can be added with minimal changes.
- Supports modular and maintainable code, which is crucial for modern software development.

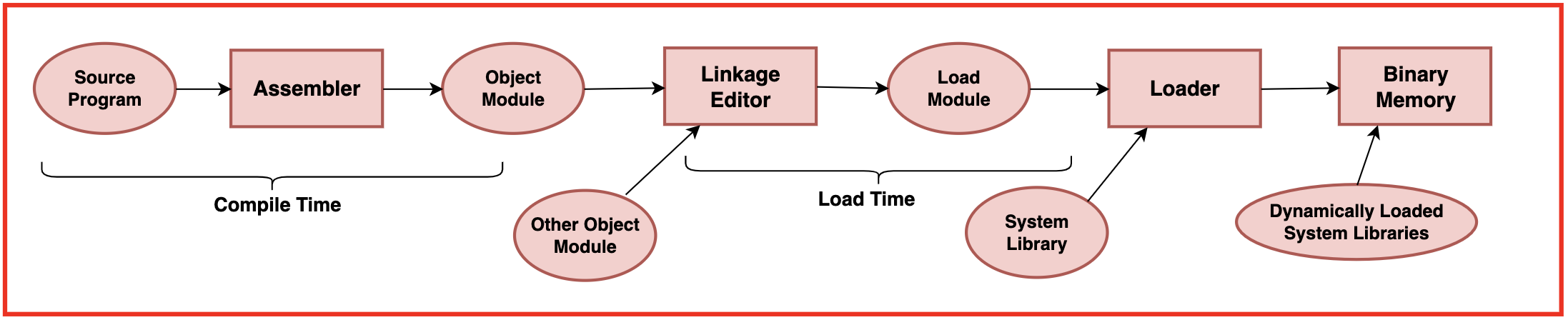
Dynamic Linking vs Dynamic Loading
Dynamic Linking links required libraries or modules to a program at runtime, instead of during compile-time. The compiler includes references to shared libraries, and the operating system loads these libraries when the program starts.
Dynamic Loading is when an application explicitly loads or unloads libraries at runtime. This is often used for loading plugins or optional modules.

Differences between Dynamic Linking and Dynamic Loading
- Dynamic Linking: Automatically managed by the OS at program start, shares library code across multiple programs.
- Dynamic Loading: Controlled by the application, ideal for plugins and modules that load based on user needs.
- Dynamic Linking saves disk space by not duplicating library code.
- Dynamic Loading is highly modular, allowing for precise control over loaded modules.
- Dynamic Linking may have version issues ("DLL Hell"), while Dynamic Loading reduces these issues.
Late Binding vs Early Binding
Late binding, or dynamic binding, happens when the method or function to be called is determined at runtime. This is common in object-oriented programming using virtual functions or interfaces.
Early binding, or static binding, happens when the method or function is determined during compilation. The method to be called is known at compile-time, which results in faster execution.
Comparison between Late Binding and Early Binding
- Late Binding: Determined at runtime, supports polymorphism and flexibility, but may have runtime errors.
- Early Binding: Determined at compile-time, faster due to no method lookup overhead, but less flexible.
- Late binding is used in languages like Python and JavaScript.
- Early binding is common in languages like Java and C# for performance-critical applications.
Benefits of Dynamic Binding
- Greater Flexibility: It allows methods to be chosen based on the actual runtime context, adapting to different scenarios.
- Supports Polymorphism: Enables different classes to be treated the same way, which allows code reuse and easier extensibility.
- Simplifies Code Maintenance: New methods can be added without changing existing code.
- Useful in Dynamic Languages: Languages that determine types at runtime use dynamic binding for flexibility.
Drawbacks of Dynamic Binding
- Runtime Overhead: Method lookup can slow down execution, which may be a concern in performance-critical applications.
- Errors Surface During Runtime: Debugging can be harder since errors are found when the program runs.
- Complex Code Management: Managing dynamic method resolution adds complexity, making code harder to understand in large projects.
- Risk of Type Errors: In dynamically typed languages, it’s easier to call methods incorrectly, leading to runtime errors.
Special thanks to Gauri Tomar for contributing to this article on takeUforward. If you also wish to share your knowledge with the takeUforward fam, please check out this article.